
The equation for the kinematics relationship between ω ω, α α, and t is Recall the kinematics equation for linear motion: v = v 0 + a t v = v 0 + a t (constant a).Īs in linear kinematics, we assume a is constant, which means that angular acceleration α α is also a constant, because a = r α a = r α. It only describes motion-it does not include any forces or masses that may affect rotation (these are part of dynamics). The kinematics of rotational motion describes the relationships between the angle of rotation, angular velocity, angular acceleration, and time. In the case of linear motion, if an object starts at rest and undergoes a large linear acceleration, then it has a large final velocity and will have traveled a large distance. Putting this in terms of the variables, if the wheel’s angular acceleration α α is large for a long period of time t, then the final angular velocity ω ω and angle of rotation θ θ are large. For example, if a motorcycle wheel that starts at rest has a large angular acceleration for a fairly long time, it ends up spinning rapidly and rotates through many revolutions. We can now begin to see how rotational quantities like θ θ, ω ω, and α α are related to each other. Table 6.2 Rotational and Linear Variables The student knows and applies the laws governing motion in a variety of situations.
Speed definition physics manual#
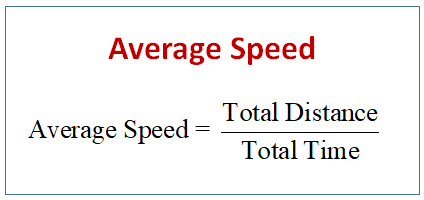
In addition, the High School Physics Laboratory Manual addresses content in this section in the lab titled: Circular and Rotational Motion, as well as the following standards: (D) calculate the effect of forces on objects, including the law of inertia, the relationship between force and acceleration, and the nature of force pairs between objects.(C) analyze and describe accelerated motion in two dimensions using equations, including projectile and circular examples.For example, if you drive to a store and return home in half an hour, and your car’s odometer shows the total distance traveled was 6 km, then your average speed was 12 km/h.The learning objectives in this section will help your students master the following standards: So average speed can be greater than average velocity, which is displacement divided by time. We have noted that distance traveled can be greater than displacement. Average speedis the distance traveled divided by elapsed time. Average speed, however, is very different from average velocity. Your instantaneous speed at that instant would be 40 km/h-the same magnitude but without a direction. Or suppose that at one time during a shopping trip your instantaneous velocity is 40 km/h due north.

At that same time his instantaneous speed was 3.0 m/s. For example, suppose the airplane passenger at one instant had an instantaneous velocity of −3.0 m/s (the minus meaning toward the rear of the plane). Instantaneous speed is the magnitude of instantaneous velocity.
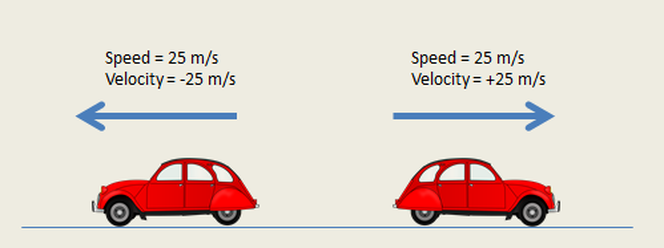
Just as we need to distinguish between instantaneous velocity and average velocity, we also need to distinguish between instantaneous speed and average speed. One major difference is that speed has no direction. In physics, however, they do not have the same meaning and they are distinct concepts. In everyday language, most people use the terms “speed” and “velocity” interchangeably. However, under many circumstances, we can find precise values for instantaneous velocity without calculus. Mathematically, finding instantaneous velocity, \(v\), at a precise instant \(t\) can involve taking a limit, a calculus operation beyond the scope of this text. (Police give tickets based on instantaneous velocity, but when calculating how long it will take to get from one place to another on a road trip, you need to use average velocity.) Instantaneous velocity \(v\) is the average velocity at a specific instant in time (or over an infinitesimally small time interval). A car’s speedometer, for example, shows the magnitude (but not the direction) of the instantaneous velocity of the car. Over such an interval, the average velocity becomes the instantaneous velocity or the velocity at a specific instant. When we carry this process to its logical conclusion, we are left with an infinitesimally small interval. The smaller the time intervals considered in a motion, the more detailed the information. \): A more detailed record of an airplane passenger heading toward the back of the plane, showing smaller segments of his trip.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
